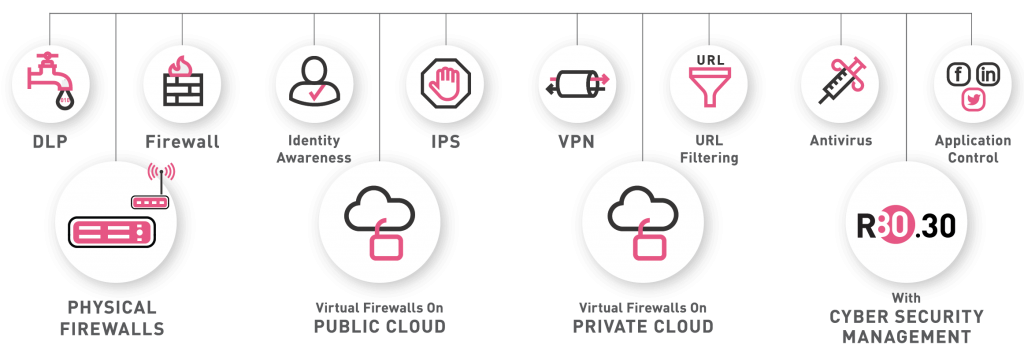
Checkpoint Firewall Provider in India
Check Point India

The Check Point Firewall & Compliance Check Software Blade protects endpoints by controlling inbound and outbound traffic and ensuring policy compliance, with centralized management from a single console. Definable zones and security levels protect endpoint systems from unauthorized access. Integrated stealth technology makes endpoints invisible to attackers. This software blade is easily managed by unified Endpoint Security Management.
We are India based Check point dealer, offers various brands of firewall solutions with best price. To know more detail about Check Point firewall contact us.
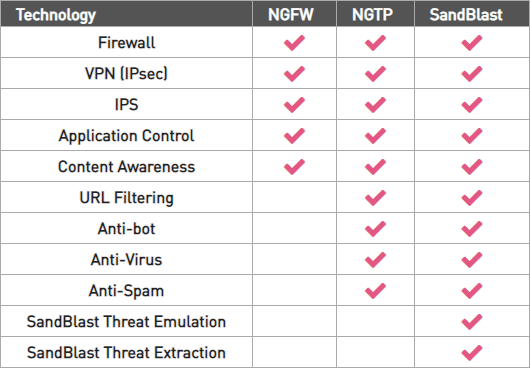
Checkpoint Next Generation Firewall (NGFW) Features
Desktop Firewall
The desktop firewall protects the integrity of endpoints by regulating inbound and outbound traffic. Definable zones and security levels prevent malware from infecting endpoint systems, block targeted attacks and stop unwanted traffic. Stealth technology makes endpoints invisible to potential attackers. Check Point leverages 17 years of Check Point firewall technology leadership.
Compliance Check
With compliance scanning, endpoint systems are scanned for compliance with corporate security policy. Systems failing compliance can be directed to remediation.Administrators can ensure that endpoints are compliant in a number of different areas including:
Centralized Management
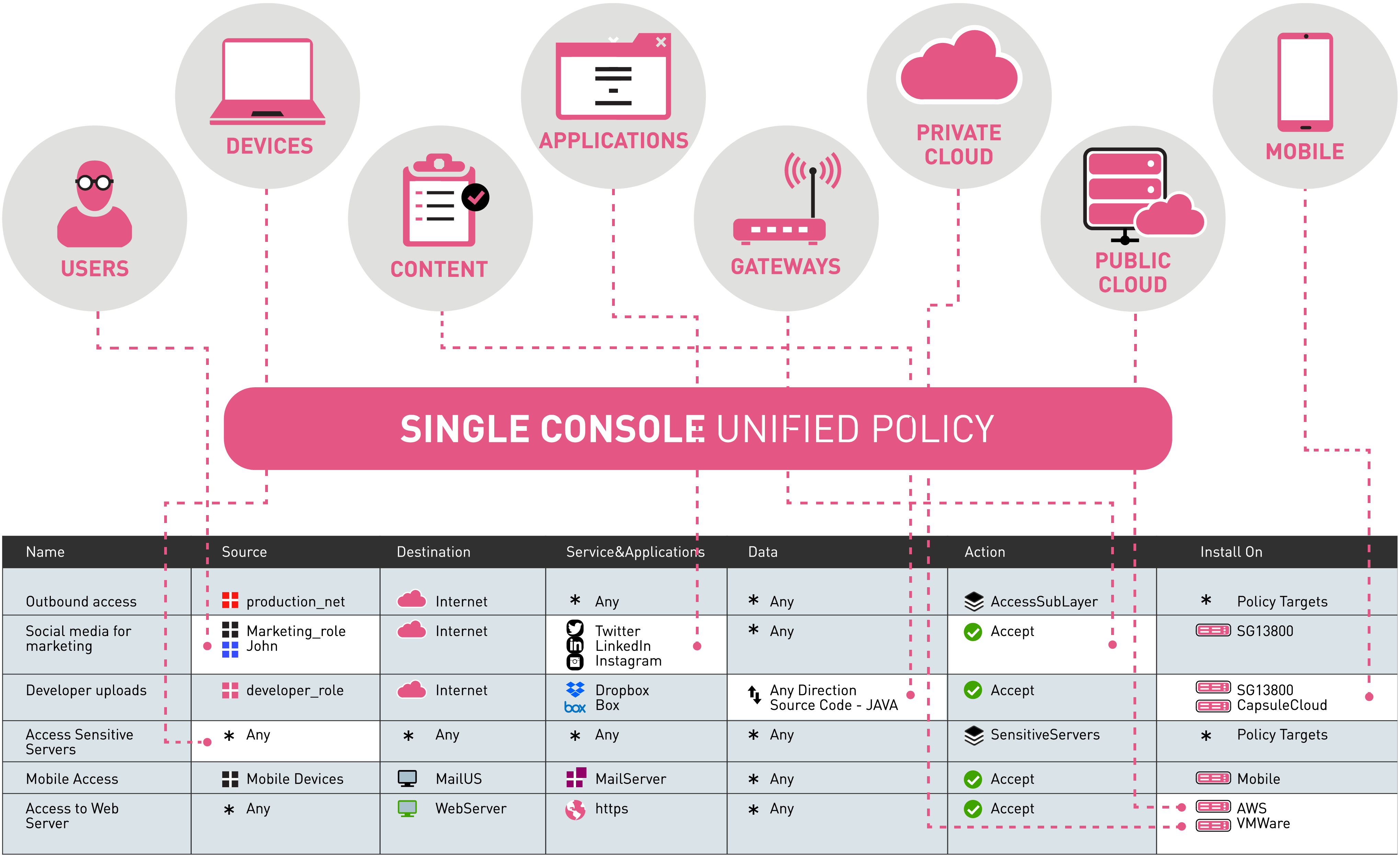
The Firewall & Compliance Software Blade is centrally managed by the Endpoint Policy Management Software Blade, enabling central policy administration, enforcement and logging from a single, user-friendly console. Centralized management offers unmatched leverage and control of security policies and multiple deployment options offer easy installation and minimize user impact, for a reduced overall cost of operations.
Integrated into Check Point Software Blade Architecture
Endpoint Security Software Blades from Check Point bring unprecedented flexibility, control and efficiency to the management and deployment of endpoint security. Choose from six Software Blades to deploy only the protection you need, with the freedom to increase security at any time from a single central management console.
A Leader in the 2018 Gartner Enterprise Network Firewall (ENFW) MQ

A Leader in the 2018 Gartner Enterprise Network Firewall (ENFW) MQ
Checkpoint Firewall Price in India
| Checkpoint Firewall | Price |
| 620 Next Generation Threat Prevention Security Appliance
The Check Point 620 appliance is an all-inclusive security appliance for small businesses (of up to 10 users). Built on the Software Blades Architecture, the 620 Appliance offers the same enterprise-class Check Point security that is used by all of the Fortune 100; on a compact desktop form factor. Hardware Specification
|
Rs.80,558/- |
|
640 Next Generation Threat Prevention Security Appliance
Hardware Specification
|
Rs. 114,038/- |
|
680 Next Generation Threat Prevention Security Appliance
The Check Point 680 appliance is an all-inclusive security appliance for small businesses (of up to 50 users). Built on the Software Blades Architecture, the 680 Appliance offers the same enterprise-class Check Point security that is used by all of the Fortune 100; on a compact desktop form factor.
Hardware Specification
|
Rs. 162,600/- |
|
770 Next Generation Threat Prevention, support and services bundle
The Check Point 770 appliance is an all-inclusive security appliance for medium size businesses. The 770 Appliance offers the same enterprise-class Check Point security that is used by all of the Fortune 100; on a compact desktop form factor.
Hardware Specification
|
Rs. 2,22,155/- |
|
790 Next Generation Threat Prevention, support and services bundle
The Check Point 790 appliance is an all-inclusive security appliance for medium size businesses. The 790 Appliance offers the same enterprise-class Check Point security that is used by all of the Fortune 100; on a compact desktop form factor.
Hardware Specification
|
Rs. 2,86,129/- |
 Firewall Firm is a Managed Cyber Security Company in India Firewall Firm is a Managed Cyber Security Company in India Firewall Firm is a Cyber Security Company in India Provides Next-Generation Firewalls for advanced protection for physical,virtual public,private cloud networks
Firewall Firm is a Managed Cyber Security Company in India Firewall Firm is a Managed Cyber Security Company in India Firewall Firm is a Cyber Security Company in India Provides Next-Generation Firewalls for advanced protection for physical,virtual public,private cloud networks