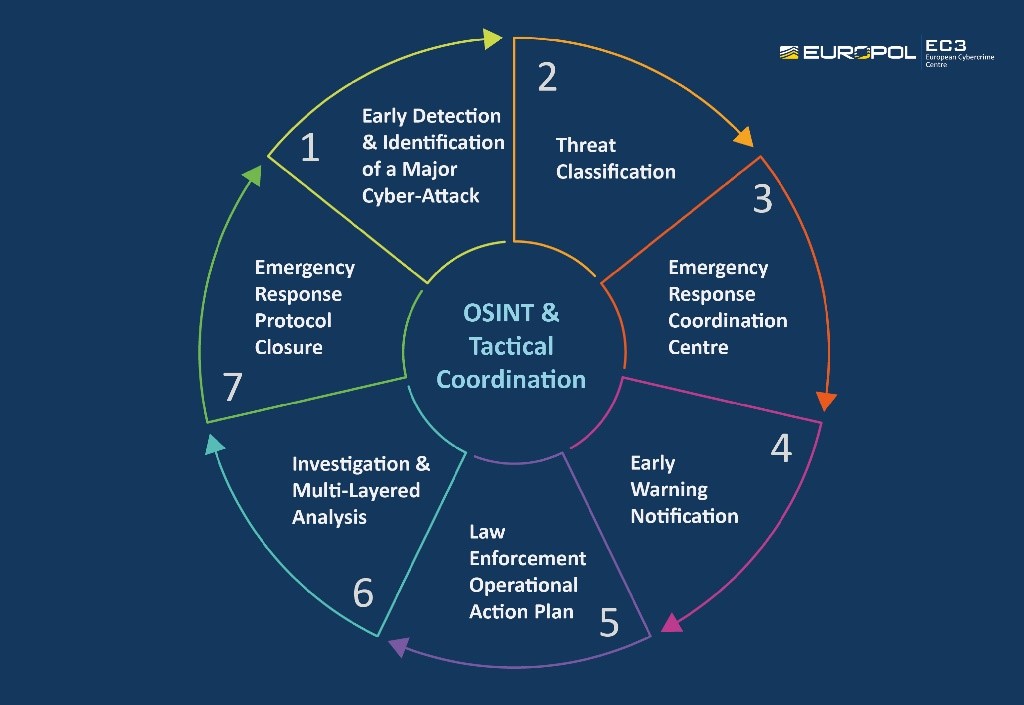
Providing enterprise network security is becoming an increasingly complex undertaking, as the number of threats emanating from the Internet continues to grow. Hackers continue to find new ways to attack systems and steal data. Dealing with these threats is highly complex. While numerous reviews like this may indicate that virtual private networks can protect you against all threats, getting on top of enterprise network security is much more difficult.
Multiple Systems
Dealing with enterprise network security means securing multiple related and connected systems, mainframes, and devices. And it doesn’t only apply to private companies – enterprise security is also applicable to organizations such as educational establishments and government departments. As networks run by these organizations grow in size and complexity, so security concerns multiply.
Virtually all enterprise systems today operate wireless networks, and this immediately compromises their security, as the wireless access point is always vulnerable to being infiltrated. Hackers have a variety of techniques available to them, such as packet sniffing, creating rogue access points, stealing passwords and other network access information, spear phishing, and so-called man-in-the-middle attacks. Each of these has the potential to compromise sensitive information, or even bring down the entire network.
Security Protocols
However, there are a variety of techniques available to help secure enterprise networks. Network security protocols are constantly evolving in order to deal with attacks, although staying one step ahead of the hackers is far from easy. This is why the contribution of white hat hackers to the security community is so valuable.
Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) incorporates the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), with the majority of enterprise security providers delivering this at 256-bit encryption level. This standard of encryption makes it practically impossible to crack the protection; even for advanced supercomputers.
Wi-Fi Alliance and WPA3
However, in June 2018, the Wi-Fi Alliance – a non-profit organization that promotes Wi-Fi technology and which is involved in the establishment of standards – certified WPA3. This will eventually replace WPA2, although this is a slow and steady process, much as the switch from 3G to 4G and then 5G takes a considerable period of time.
However, although encryption is extremely valuable, it is just the start of securing an enterprise network. Second, on the list of priorities should be the deployment of a wireless intrusion detection system (WIDS) and a wireless intrusion prevention system (WIPS). These are network devices that continually monitor traffic and activity on Wi-Fi networks, and help recognize and eliminate unauthorized access.
Regular Patching
IT professionals responsible for network security should also ensure that all software and hardware is patched on a regular basis. Updating software, in particular, is absolutely critical, as vulnerabilities appear in even the best-known programs with alarming regularity. You simply must be running the most up-to-date and fully patched programs, otherwise, you run the risk of completely compromising all other security measures taken. All it takes is for hackers to exploit one known vulnerability, and you can be rapidly up a creek without a paddle.
Security Standards
As the authorities attempt to assist businesses in protecting their data, so a range of security standards have been established. One of these is the Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) 140-2 compliance for encryption, which can be considered particularly important for enterprise networks, which require particularly robust encryption. You should ensure that your network is fully compliant with this standard. And if you’re unsure how this is to be achieved then don’t shy away from contacting the authorities, as they will be more than happy to assist you.
Training Employees
The next port of call for all enterprise security should be dealing with everyday members of staff. This is where things can go horribly wrong. There are other things you can implements which we’ll get on to in a minute, but first of all, make sure staff are on the same page as you. Emphasize to employees that security is all important, and don’t neglect training them in network security principles. Again, your network is only as secure as the weakest password, and the laxest worker, so make sure everyone is trained up and diligent.
Multi-Factor Authentication
And while you’re at it, ensure that you initiate multi-factor authentication across your network. This just makes it so much harder to crack your enterprise system. Strong passwords combined with multiple layers of security and authentication will simply make your network way more secure.
Secure Protocols
Another layer of security that you can consider is a bit of a mouthful…namely, Extensible Authentication Protocol-Transport Layer Security! This is another authentication framework that makes it harder for attackers to gain access to your network, and it also helps enhance authentication transaction and communication.
There are other protocols that can be used as well, but one final process that we’d like to mention is the implementation of a guest Wi-Fi network. This can be kept separate from the main network, providing a vital failsafe mechanism for network security. By employing routers with multiple Service Set Identifiers you can isolate your valuable enterprise network access points, and ensure that your key data is kept under lock and key.
Keep Renewing
Finally, we should mention the importance of continually renewing your approach. This is one area where you can’t stand still, as hackers and network attackers are continually crafting new approaches to circumventing security. You must keep up-to-date with all of the latest security and encryption technology, and ensure that it is implemented across your network.
 Firewall Firm is a Managed Cyber Security Company in India Firewall Firm is a Managed Cyber Security Company in India Firewall Firm is a Cyber Security Company in India Provides Next-Generation Firewalls for advanced protection for physical,virtual public,private cloud networks
Firewall Firm is a Managed Cyber Security Company in India Firewall Firm is a Managed Cyber Security Company in India Firewall Firm is a Cyber Security Company in India Provides Next-Generation Firewalls for advanced protection for physical,virtual public,private cloud networks